Founded in 1990, Sharpe Products is an ISO 9001:2015 certified company specializing in industrial and commercial pipe and tube bending, laser cutting, end-forming or other custom fabrication services. In addition, we offer a robust line of architectural handrail fittings and accessories such as brackets, connectors, disks, end-caps, flanges, newel caps and spheres.
Founded in 1959, Tube Bending Technology has its roots in the Apollo space program. With such a legacy, we take quality, performance and customer satisfaction very seriously. Our custom tubing services include tube bending and coiling, end finishing, processing, machining, welding/brazing, helium leak detection and more. At TBI, we live and breathe quality. To show our commitment, we are ISO...

At KMK Metal Fabricators, Inc., we pride ourselves on being industry leaders in tube fabrication, offering a comprehensive range of services tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clients. With years of experience, a commitment to excellence, and a customer-centric approach, we have established ourselves as a trusted partner in the fabrication industry. Our core focus lies in providing...

SCR Precision Tube offers the best customer service in the industry, specializing in prototyping & design of tube, hose & fittings assemblies. Our CNC facility has full tube bending, cutting & swagging capabilities with elbows & straight tubing in steel, aluminum, copper & titanium. Email for a quote!

At TBC Metalworks, we take pride in our expertise in tube fabrication, offering tailored solutions to meet the diverse needs of our clients across various industries. With years of experience, a commitment to quality, and a customer-centric approach, we have established ourselves as a trusted partner in the fabrication industry. Our primary focus is on providing a comprehensive range of tube...

More Tube Fabrication Companies
Tube fabrication is a process of shaping, cutting, and bending metal tubes into custom shapes and sizes for various applications. It has been used for centuries to create a wide range of products, from simple household items to complex machinery parts. The history of tube fabrication dates back several centuries, with evidence of tube bending and shaping techniques used in ancient civilizations such as Rome and Egypt. The process of tube fabrication evolved over time as new materials and techniques were developed.
One of the earliest recorded uses of tube fabrication was in the production of armor and weapons during the medieval period. During the Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries, tube fabrication became an essential part of manufacturing, particularly in the textile and locomotive industries. New machinery and techniques were developed to create tubes of various shapes and sizes for use in steam engines, boilers, and other industrial applications. In the early 20th century, the invention of the automobile further drove the demand for tube fabrication, particularly in the creation of exhaust systems and other automotive components. Today, tube bending machines are used to create complex shapes and designs as the process has become more advanced with the introduction of new techniques and materials.
The Process of Tube Fabrication
Tube fabrication is a complex process that involves several steps to create custom shapes and sizes of metal tubes. Here’s a more detailed overview of each step in the process:
Material selection: Material selection is the first step in the process of tube fabrication. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the application, considering factors such as strength, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and compatibility with fluids or environments. Common materials used in tube fabrication include metals like steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium, as well as plastics such as PVC, polyethylene, and nylon. Each material has its own set of advantages and limitations. For example, steel is known for its high strength and durability, making it suitable for demanding applications. Stainless steel, meanwhile, offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments. Aluminum, on the other hand, is lightweight and has good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for industries like automotive and aerospace. The selection of the appropriate material involves considering factors such as mechanical properties, chemical compatibility, cost, availability, and any specific industry standards or regulations that need to be met. By carefully choosing the right material, tube fabricators can ensure that the fabricated tubes meet the required performance criteria and deliver optimal functionality and longevity.
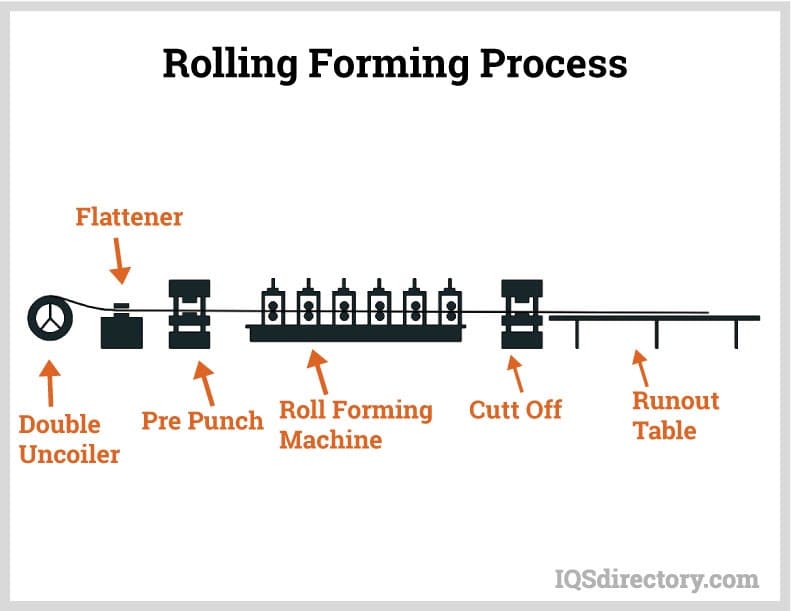
Cutting: Cutting is the next step in the tube fabrication process, where the selected material is shaped and prepared for further processing. Various cutting methods can be employed depending on the material type, thickness, and desired precision. Traditional cutting techniques include sawing, shearing, and manual cutting using tools like hacksaws or pipe cutters. However, modern tube fabrication often involves advanced cutting methods such as laser cutting, plasma cutting, or water jet cutting. Laser cutting utilizes a high-powered laser beam to precisely melt, vaporize, or burn through the material along the desired cutting path. Plasma cutting uses a plasma torch to ionize gas and create an electrically conductive plasma arc that cuts through the material. Water jet cutting employs a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to erode the material and create clean, accurate cuts. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology is often utilized to control these cutting processes, ensuring precise and repeatable cuts. The choice of cutting method depends on factors such as material type, thickness, complexity of the cut, and production volume. Accurate and clean cutting is essential to achieve the desired dimensions and prepare the material for subsequent fabrication steps.
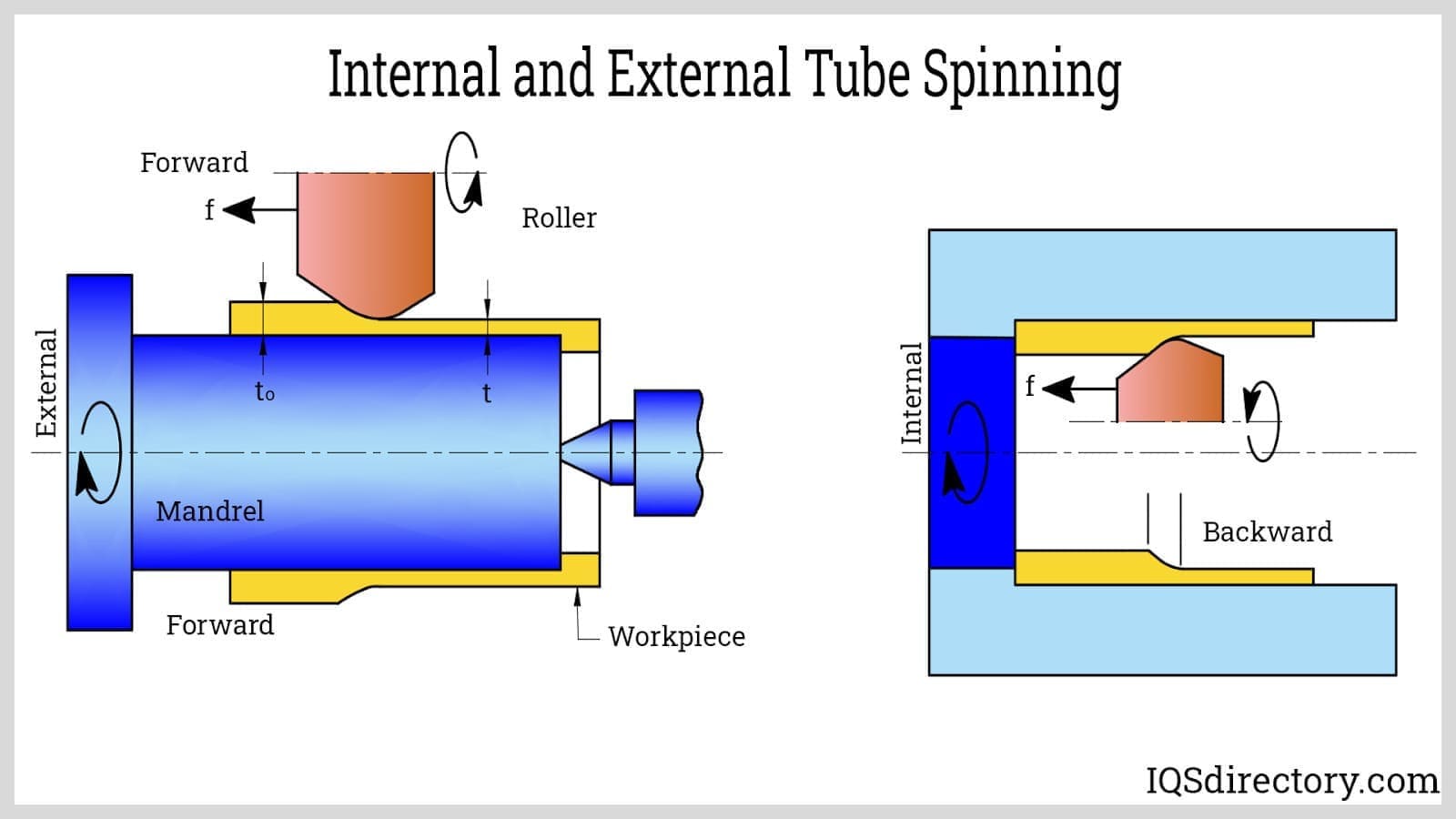
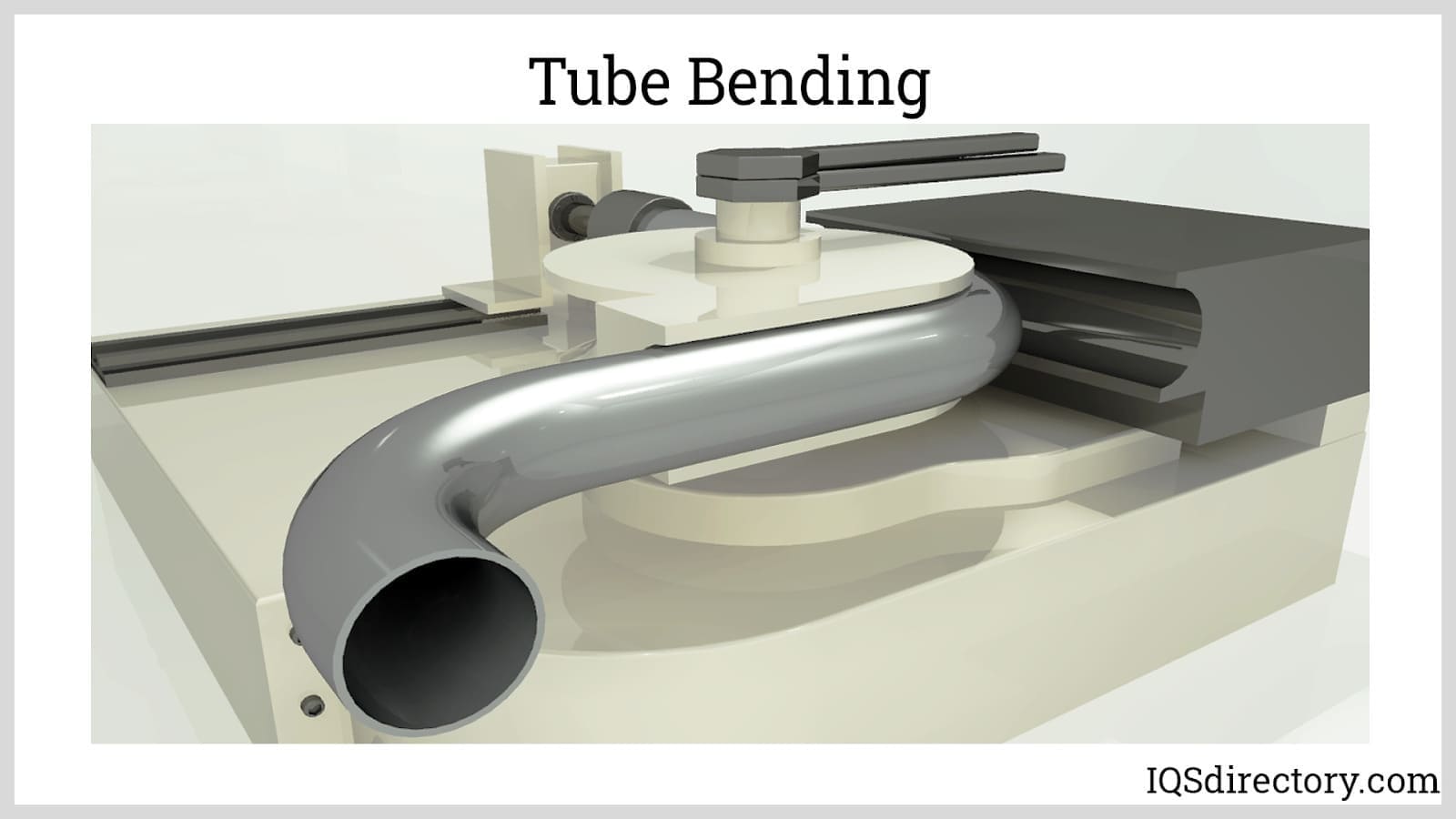
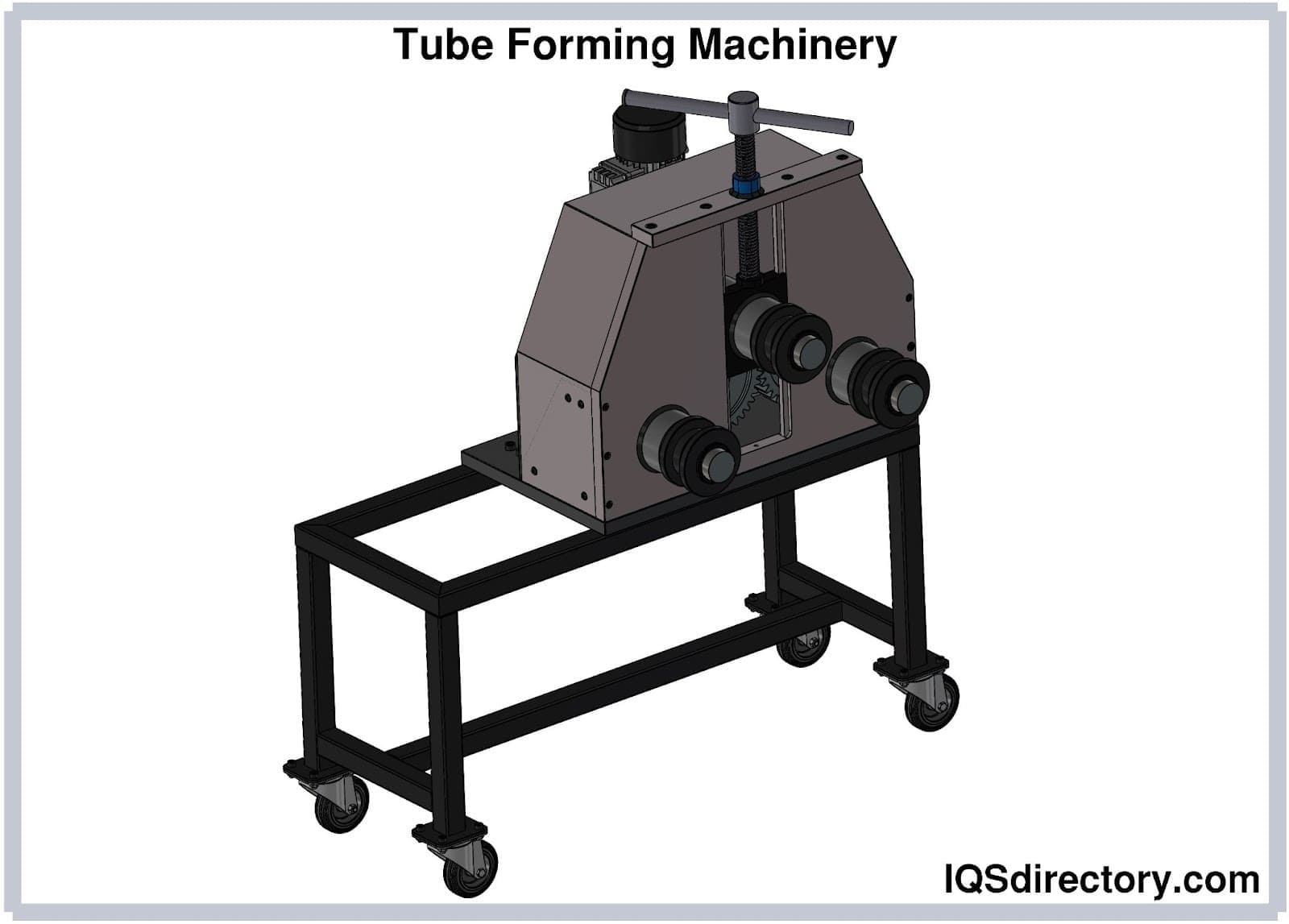
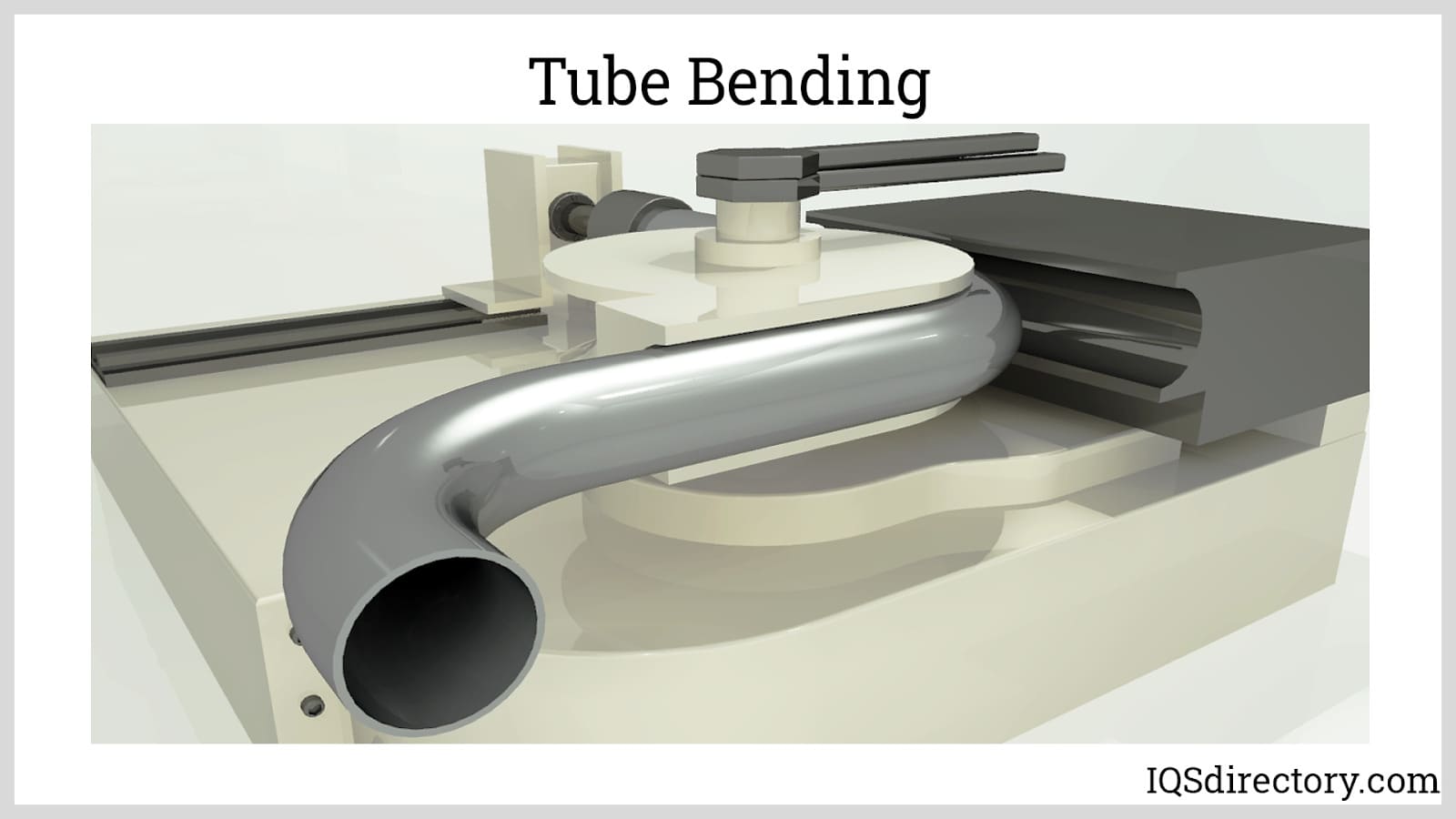
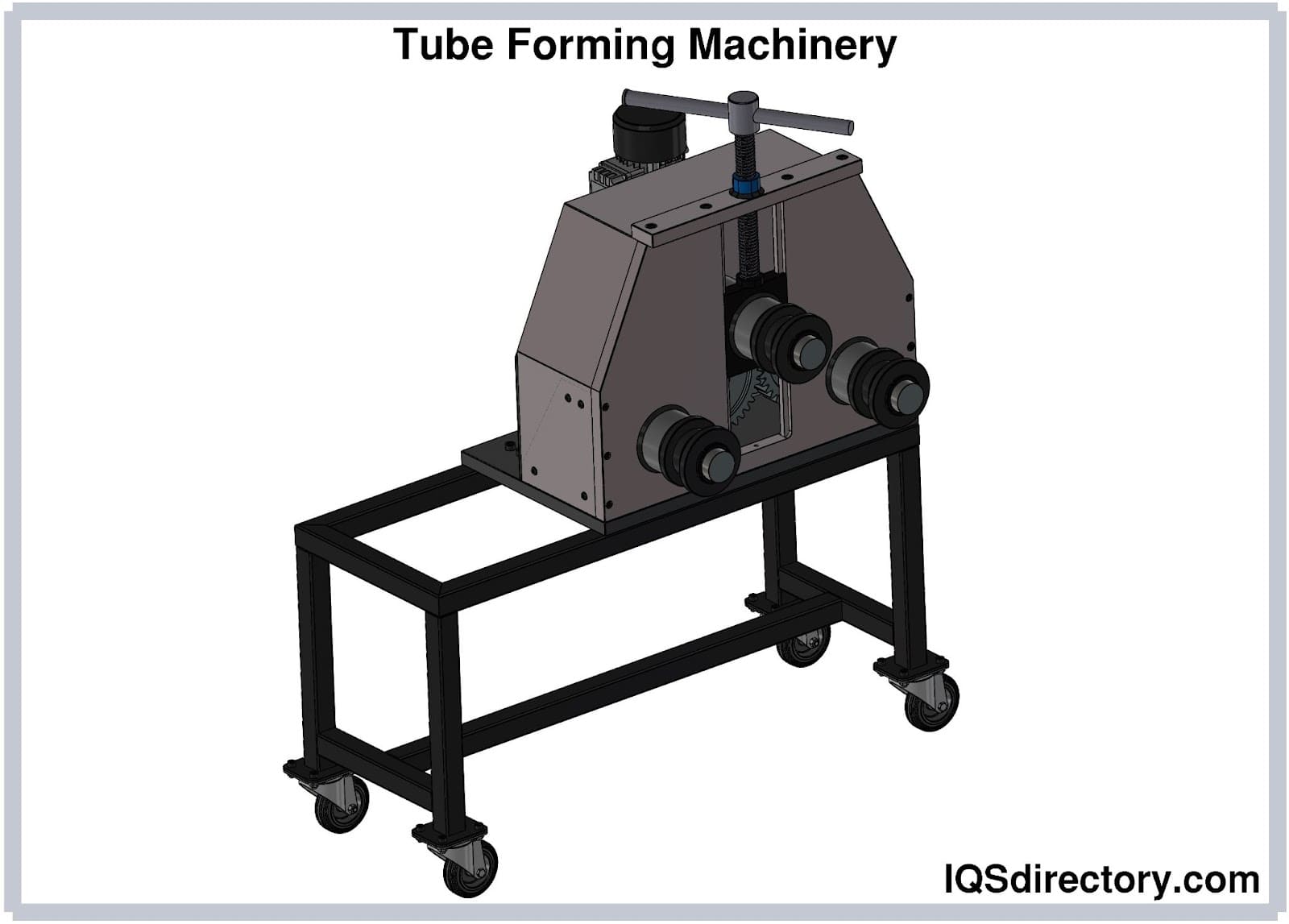
Shaping: Shaping is a fundamental step in the tube fabrication process, where the cut material is transformed into the desired tube form. There are several methods used for shaping tubes, depending on the desired geometry and material properties. One common shaping technique is bending, which involves applying force to the tube to create curved or angled sections. Bending can be done manually or with specialized equipment like tube bending machines. Another shaping method is rolling, where the tube is passed through rollers that gradually shape it into a cylindrical form. This process is often used to create long, continuous tubes with consistent dimensions. Extrusion is another shaping technique that forces the material through a shaped die, creating a tube with a specific cross-sectional shape. This method is particularly suitable for producing tubes with complex profiles or non-circular shapes. Additional shaping processes may include flaring, swaging, or expanding the ends of the tube for improved connections or joining with other components. The choice of shaping method depends on factors such as the desired tube geometry, material properties, production volume, and equipment availability. Accurate shaping ensures that the fabricated tubes meet the required dimensions and functional requirements for their intended applications.
Welding: Welding is the next step in tube fabrication, particularly when joining multiple tube segments together or attaching other components. Welding involves the fusion of materials through the application of heat, resulting in a permanent bond. Various welding techniques can be employed depending on the materials used, joint design, and desired strength. Common welding methods for tube fabrication include TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, and laser welding. TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce a precise and high-quality weld, making it suitable for thin-walled tubes and critical applications. MIG welding utilizes a consumable wire electrode and an inert gas shield to protect the weld pool, providing high-speed and efficient welding for thicker tube walls. Laser welding utilizes a focused laser beam to melt and fuse the materials, offering precise control and minimal heat input. Welding parameters such as heat input, welding speed, and filler material selection are carefully controlled to ensure proper fusion, structural integrity, and durability of the welded joint. Skilled welders, proper joint preparation, and stringent quality control measures are essential to achieving strong and reliable welds in tube fabrication. Welding ensures the integrity of the fabricated tubes and enables the assembly of complex tube structures for various applications.
Finishing: Finishing is a critical step in the tube fabrication process that takes place after welding and involves various processes to enhance the appearance, functionality, and durability of the fabricated tubes. The specific finishing techniques employed depend on the desired surface characteristics and the requirements of the application. One common finishing process is polishing, which involves removing any surface imperfections, such as burrs or rough edges, and creating a smooth and reflective surface. Polishing can be done through mechanical means using abrasives or through chemical processes. Another common finishing technique is coating or plating, where a protective layer is applied to the surface of the tube to enhance corrosion resistance, improve aesthetics, or provide specific functional properties. Coatings can include paint, powder coating, anodizing, or specialized coatings like zinc or chrome plating. Additionally, surface treatments such as passivation or electropolishing can be used to improve the corrosion resistance of metal tubes. Laser marking or engraving may also be employed to add permanent markings or identification labels to the tubes. These finishing processes not only enhance the visual appeal of the tubes but also improve their longevity, resistance to environmental factors, and overall quality.
Quality control: Quality control is the final step in the tube fabrication process and is essential in order to ensure that the fabricated tubes meet the required specifications, standards, and customer expectations. It involves implementing rigorous measures to monitor and evaluate various aspects of the fabrication process. Quality control begins with thorough inspection and verification of raw materials to ensure they meet the desired quality and specifications. Throughout the fabrication process, inspections are conducted at critical stages such as cutting, shaping, welding, and finishing to check for dimensional accuracy, structural integrity, and adherence to design requirements. This can involve visual inspections, measurement checks, non-destructive testing, and other quality assessment techniques. Advanced inspection tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), laser scanners, and ultrasonic testing equipment may additionally be employed for precise measurement and defect detection. Furthermore, samples may be subjected to destructive testing to assess mechanical properties and verify weld integrity. By implementing robust quality control protocols, fabricators can identify and address any deviations or defects promptly, ensuring that the final fabricated tubes meet the highest standards of quality, reliability, and performance.
Limitations and Negatives of Tube Fabrication
Tube fabrication, while offering numerous advantages, also comes with several negative considerations. The cost of tube fabrication can be significant, especially when specialized equipment, materials, and skilled labor are involved. The fabrication process can be time-consuming, particularly for complex designs or multiple production steps. Material waste is another concern, as offcuts and scrap can be generated during fabrication, requiring proper management and recycling. Design limitations may also restrict the possibilities for certain tube geometries or intricate shapes. Maintaining consistent quality throughout the fabrication process can be additionally challenging, requiring robust quality control measures. However, despite these considerations, tube fabrication remains a crucial process for many industries, and ongoing technological advancements aim to address these concerns and improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Overcoming These Limitations
Tube fabricators have implemented various strategies to address the negative considerations associated with the fabrication process. They optimize their production processes through the use of advanced machinery and automation technologies, aiming to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize material waste. Rigorous quality control measures, including advanced inspection tools and adherence to industry standards, are additionally implemented to ensure consistent product quality. Fabricators also focus on material optimization, exploring techniques to maximize material utilization and minimize waste. Collaboration with customers during the design phase helps identify and address fabrication challenges early on, optimizing the manufacturability of the tubes. Finally, continuous training and skill development programs are in place to enhance the expertise of the workforce. These efforts collectively contribute to improved efficiency, cost-effectiveness, quality, and sustainability in tube fabrication.
Benefits of Tube Fabrication
Tube fabrication offers numerous benefits across various industries. To start, it provides versatility in design and functionality. Tubes can be fabricated in a wide range of sizes, shapes, and materials to suit specific applications, whether it’s for structural support, fluid or gas transportation, heat exchange, or electrical conduits. Additionally, tube fabrication enables customization and tailor-made solutions. Fabricators can create tubes with precise dimensions, complex geometries, and specialized features to meet specific requirements and optimize performance. Likewise, fabricated tubes exhibit excellent strength and durability, making them suitable for demanding environments and applications. They can withstand high pressure, temperature, corrosion, and mechanical stresses, ensuring long-term reliability. Tube fabrication also allows for efficient material utilization and lightweight designs, contributing to cost savings, fuel efficiency, and reduced environmental impact. Furthermore, the fabrication process enables seamless integration with other components or systems, facilitating easy assembly and installation. Overall, tube fabrication plays a vital role in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing, providing solutions that enhance performance, efficiency, and safety.
Applications of Tube Fabrication
Tube fabrication finds widespread applications across multiple industries. In the automotive sector, fabricated tubes are utilized in exhaust systems, fuel lines, brake lines, and cooling systems. They contribute to the efficient routing and transport of fluids while withstanding high temperatures and pressures. In the aerospace industry, tube fabrication plays a crucial role in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, fuel lines, and structural components. Precision-fabricated tubes ensure reliability, weight reduction, and efficient fluid distribution in aircraft and spacecraft. The construction industry extensively employs tube fabrication for applications such as scaffolding, handrails, and support systems. Tubes provide strength, durability, and design flexibility, enhancing the safety and functionality of buildings, bridges, and infrastructure projects. HVAC and refrigeration systems rely on tubes for the smooth flow of air, refrigerants, and fluids, contributing to temperature regulation in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Tube fabrication is also essential in the medical field, where it is used in surgical instruments, catheters, endoscopes, and fluid management systems. In the oil and gas industry, tubes are crucial in drilling operations, well completion, and fluid transportation. They withstand high pressures, corrosive environments, and extreme temperatures, ensuring the safe and efficient extraction and transportation of hydrocarbons. Additionally, tube fabrication finds applications in various industries, including industrial and manufacturing processes, marine applications, food and beverage processing, furniture manufacturing, agricultural machinery, sports equipment, and artistic installations. The versatility, strength, and customization options offered by fabricated tubes make them essential components in numerous industries, contributing to improved performance, efficiency, and safety in various applications.
Choosing the Right Tube Fabrication Company
To ensure you have the most beneficial outcome when choosing a tube fabrication company, it is important to compare several businesses using our directory of tube fabrication companies. Each tube fabrication company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each tube fabrication business using our proprietary website previewer to quickly learn what each business specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple tube fabrication companies with the same form.
Check out our Roll Forming website
Check out our Forgings website



 Broaching
Broaching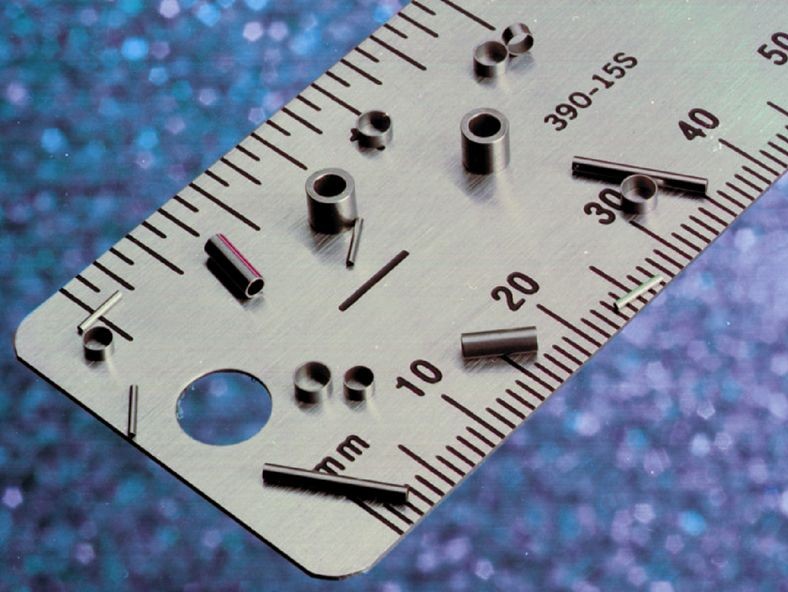 CNC Machining
CNC Machining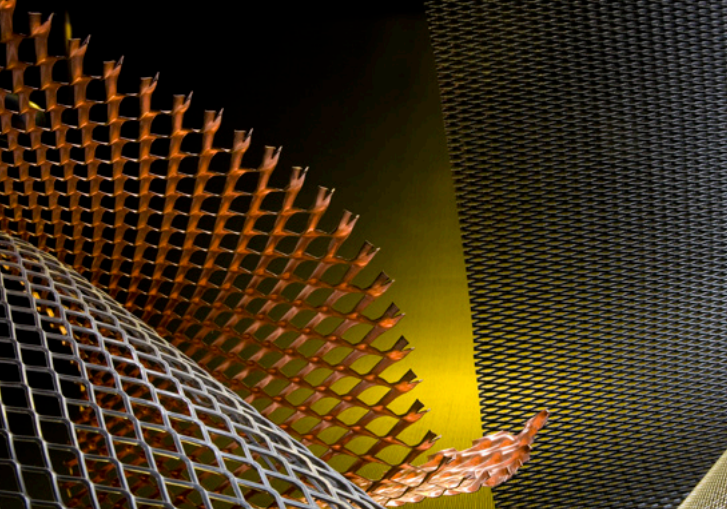 Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting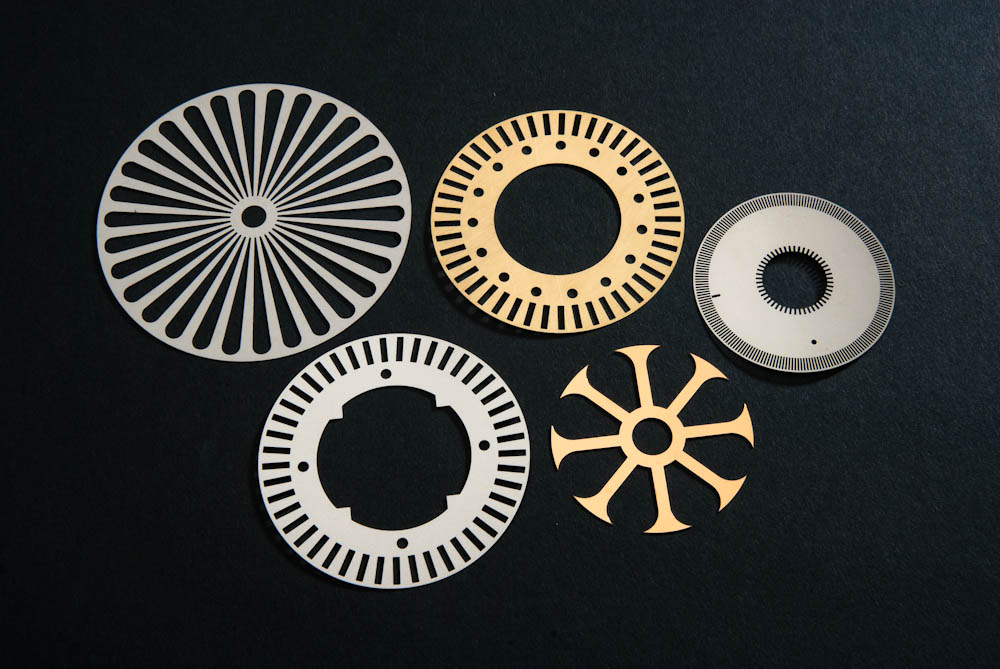 Metal Etching
Metal Etching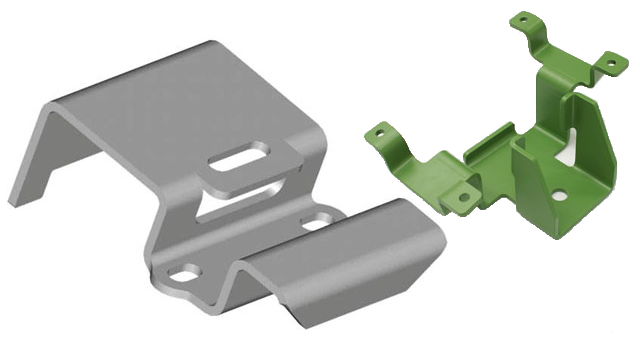 Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services